This is a hight level overview of Amazon web services (AWS)
Thoughts
- Shift in mindset
- Back then as a “developer” optimation based on
performace is good enough, but now
Cost + Performaces needs to be jointly optimized. - Building service base on value
- This forces the designers of a system to think the literal value created from the service to justify its cost.
- Trend
- Physical machines -> Virtual machines -> Containers -> Serverless
Basics
Where are these service physically store?
Regions
- Paris
- London
- Dublin
- Tokyo
- Ohio
Availability zone (AZ)
- One or more data centers are present here.
- Its best practice to spread apart the application to run in different AZ as a disaster recovery plan.
Factors to consider when selecting a service.
- Compliance
- Proximity to customers
- Feature availability and
- Cost per region.
What API exists?
Access AWS via the following
- AWS console web
- SDK
- CLI
Hard/ Soft limits of services
Knowing hard / soft limits of each services
- For S3, Hard limit 5T size of a single file.
- Lambda, Soft limit compute to 15 min (Subject to 10GB memory as of 2023-03)
Compute resources
Elastic compute cloud (EC2)
- Optimized for
- Compute
- Memory
- Storage
- Hardware acceleration
- Unmanaged
- OS level access
- Virtual machines (Nitro) as AWS custom solution
Serverless
- Lambda
- Design the trigger
- Managed (Auto scales)
- Process which runs < 15 mins
- Fargat
- Container based
- Managed
Containers
- Elastic Kubernaties Service (EKS)
- Elastics container Service (ECS)
On perm solution
- Amazon Outpost
Orchestrate resources
- Beanstalk Manages resources and auto scaling of web applications
- Cloud Formation Template based (similar to terafarm)
- AWS systems manager Consumes Chef recipes and Ansable playbook.
Work load at scale
- Region level
- R53 ( Using DNS routing ) across multiple regions.
- AZ level
- ELB (Load balancer) for with in the region.
Elastic Load Balancing (ELB)
- Managed
- Auto scales only with in the same region
Sending Messages
- Simple Queue Service (SQS)
- Send, Store, Receive Messages (In Queue)
- FIFO
- Standard
- Managed
- Send, Store, Receive Messages (In Queue)
- Simple Notification Service (SNS)
- Publish and Subscribe model (SLA are approximately meet)
- Pull based model for receiving the message
Networking
Virtual private cloud (VPC)
- Subnet (reserved IP address for grouping resources together)
- public (access to Internet)
- private
- Subnet (reserved IP address for grouping resources together)
Gateways is required to access VPC
- Internet Gateway (IGW) (anyone from public)
- Virtual Private Gateway (logged-in user)
Subnet communications
Network access control list (ACL) (Stateless):
Checks packetsentering inside and existing outside of thesubnet with ACL, since its stateless.Security group (State-full): Is for
Instance level(say ec2) access for inside and outside. By default- Blocks all input packets (need to specifically configure the list of approved packets)
- Allows all packets output bound.
AWS Direct connect
On prem -> AWS VPC (Physical cable) in partnership with network cable provider (say BT in UK)
- Dedicated
- Hosted (shared across other users)
Route 53
- Buy domain names
- Different routing policies
- Latency based
- Geolocations DNS
- Geo proximity routing
- Weighted round robin
Storage
Instance store volumes: physical storage for EC2 instance. Use it for temp storage.
Services
- Elastic Block Store (EBS)
- EBS volumes are virtual storage (Fixed)
that persists data across the life cycle of EC2 instances.
- Accessible only with the same AZ.
Configure by:
- Size.
- Type.
- Configuration.
Takes incremental backups of data (snapshots)
- Simple Storage Service (S3)
- Each data is stored in a bucket;
Policies can be configured to move across below services like Glacier.
- S3 Infrequent access (S3 IA)
- To achieve the data; and have policies like Write once and read many (WORM) on the vaults.
- Elastic File System (EFS)
- Linux File System ( Like NFS)
- Accessible only with the same Region (ie Multiple AZ).
- Auto scale to meet demand with multiple EC2 instance reading from EFS (Managed).
Content delivery network (CDN) - Cloud front: Configure 1. Edge location (Physical locations different from regions) 2. Cache neat customer 3. Time to live
Database
Services
Relational Database Management Service (RDBMS)
- MySQL
- PostGreSQL
- Oracle and so on.
Relational Database Service (RDS)
Amazon Aurora (SQL)
- Cost effective
- Hight availability
DynamoDB
- Serverless DB (Managed)
- Backs up
- NoSQL (Hight Performance).
Redshift; Big data/Data warehouse
Database Migration service Homo - On prem SQL to AWS SQL Hetro - SQL to No SQL
Document DB
Neptune (Graph DB)
Quantum ledger DB; for immutable data.
DB Accelerators (Elasticache)
- Mem cache
- Redis
- For DynamoDB; DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX)
Security
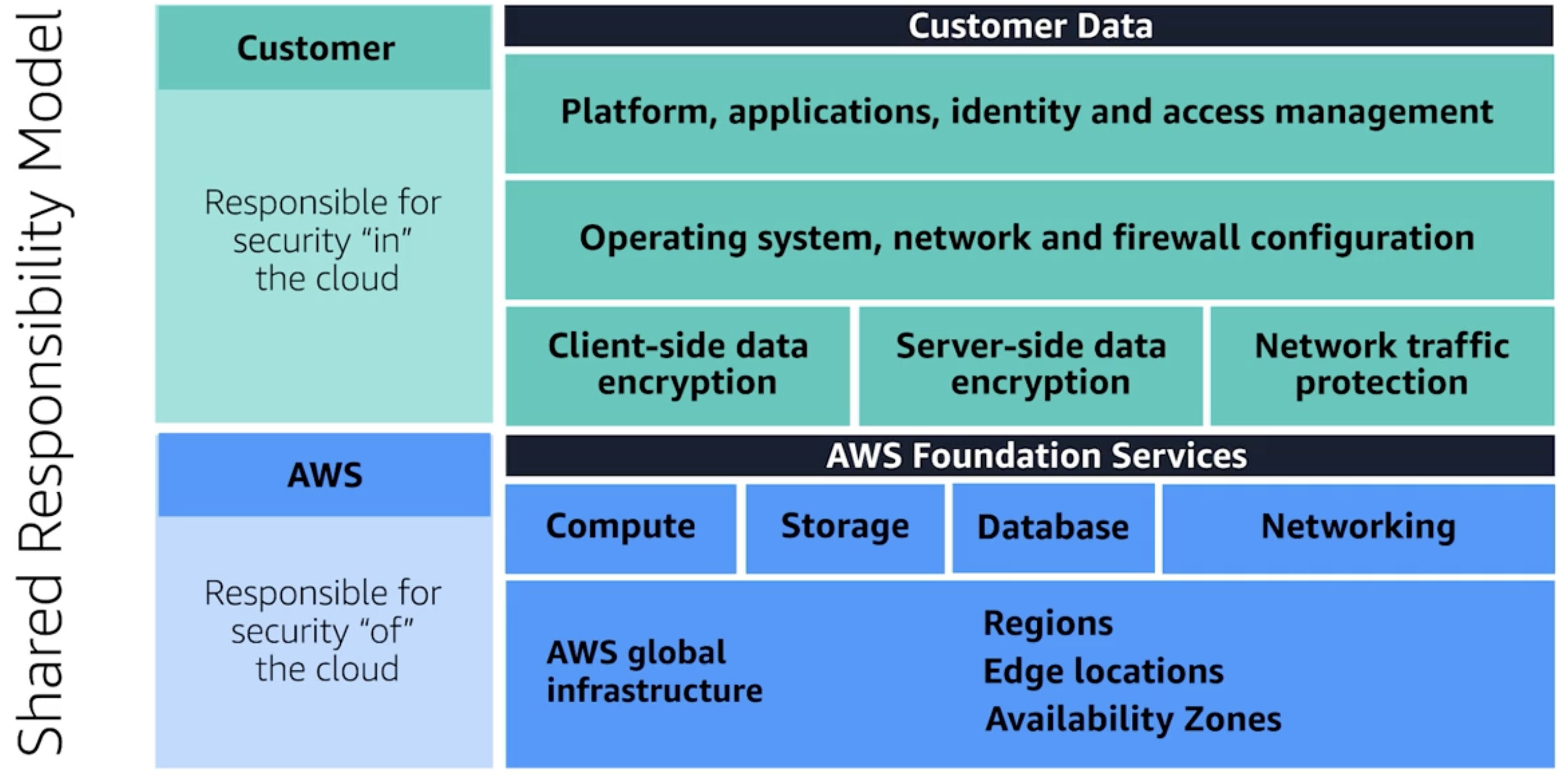
Shared responsibility of security
- Hardware by AWS
- OS/Software for Users
Permission for users
- IAM root user
- Can access and control any resources.
- Multi factor authentication
Services
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Users; By default has no permission (least privilege).
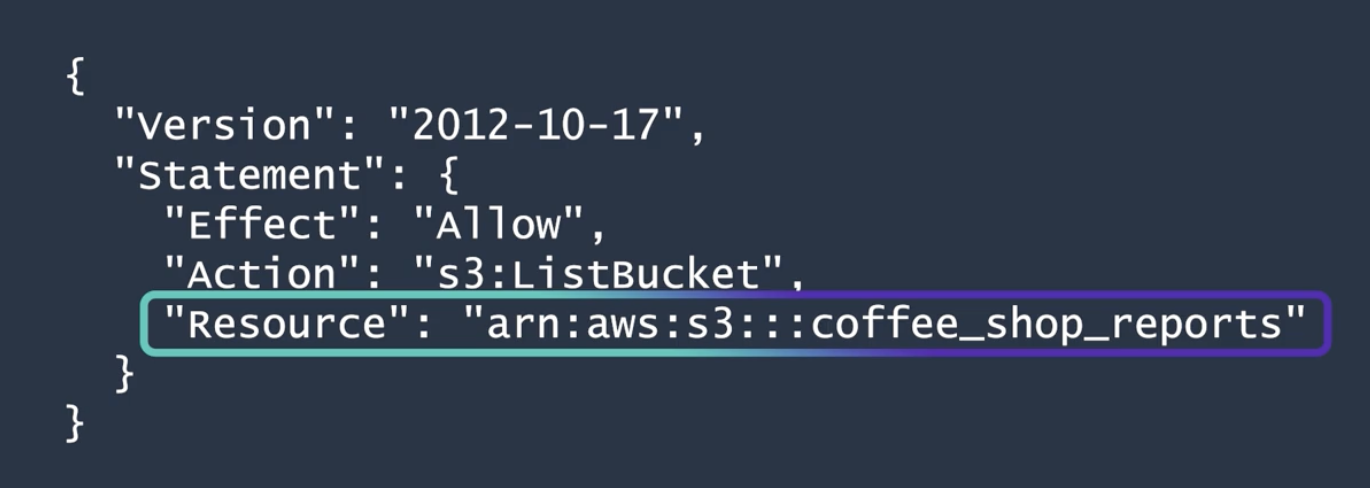
IAM policy is a json file with the following Effect: Allow or Deny. Action: Any AWS API call. Resource: Which AWS resource the API call is for.
IAM Groups; collection of users Can attach policy to group
IAM roles; takes temporary permission for that role. To access applications; external identities; aws resources; and services Similar to sudo as root user.
AWS Organization
- Manage multiple accounts from this service.
- Consolidated billing
- Compliance and security
- Accessing resources
- Service control policies (SCPs) managing policies for members account (users/roles) that can access resources/services.
AWS compliance
- Documentations on security and white paper.
- For reports from 3rd party auditors
Type of attacks
- Distributed denial of service (DDoS)
- UDP Flood
- HTTP Level attacks
- Slowloris attack
AWS Shield with AWS WAF
- WAF
- web application firewall (filters signature of bad actors)
- Shield
- Use ML to actively monitor threads/bad actors
AWS Key Management Service (KMS)
Encryption at
- Rest :: DynamoDB uses it with KMS
- Transit :: Data from one service to an other uses
Secure Sockets Layer(SSL) to transmit.
Inspector
- Automated security analysis.
- Provides report on best practice with setting up service.
GuardDuty
Real time meta data from most primary services is used to detect vulnerabilities with ML.
- Works in parallel to existing service with out affecting its performance/availability.
Monitoring and analytics
CloudWatch
Real time monitoring of AWS services
- CloudWatch alarm
- Trigger based on arbitrary variable threshold.
Has
SNSintegration to send messages as well. - CloudWatch dashboard
- to real time visualization of data
Reduce Mean time to resolution (MTTR) and improve Total cost of ownership (TCO)
CloudTrail
- Logs each actions (API calls) for any services used
- Used mainly for auditing.
Trusted Advisor
Some are free, but some depends on your support plan.
Following are the factors taken into account when analyzing your services.
- Cost optimization
- Performance
- Security
- Fault tolerance
- Service limits
Based on the recommendations one can take actions to optimize.
Pricing
- Pay as you go.
- Variable to consider
- Regional cost
- Variable to consider
- Pay less with reserved.
- Pay less with volume based discount.
Types of “Free” plans
- Lambda
- Under 1 million invocations its free.
- S3
- 12 months free up to 5 GB.
- Lightsail
- 1 month trail of 750 hr of usage.
Pricing Calculator
- Helps with estimating the price of running joint service. https://calculator.aws/
Billing
- Consolidated billing with AWS Organization
- Refer to https://docs.aws.amazon.com/awsaccountbilling/latest/aboutv2/consolidated-billing.html
- Get alerts based on certain threshold.
- Report for visualizing the cost across time.
Support plan
- Basic
- Few tools
- Developer
- Email support
- Business support
- Phone call
- Enterprise Support
- 15 min SLA
Marketplace
Vetted 3rd part software/click and go services available in market place with pricing to chose. https://aws.amazon.com/marketplace
Cloud Migration
Cloud Adoption Framework (Action plan)
- Non Technical
- Business, People, and Governance
- Technical
- Platform, Security, and Operations
6R’s of migration
RehositingMove existing applications to cloud with no optimizations (Lift and shift).ReplatformingMove on component like DB to aws service (with no code changes)RetireDeprecate applications that are not required any more.RetainNeeded for a smaller period of time (will Retire later on).RepurchasingNewer application over old applicationRefactoringNew code
Snow family
Move data physically via an edge device (ship to back to aws) when it takes longer to transmit it over the network.
Snowclone
- 2 CPUs, 4 GB of memory, and 8 TB of usable storage
Snowball
- Snow ball edge compute optimized
- 52 vCPU
- Snow ball edge storage optimized
- 80 TB
Snowmobile
Shipping container worth device (100PB of data).
Well Architected Framework
A tool that provide a report on the following principles;
- Operational Excellence
- Security
- Reliability
- Performance Efficiency
- Cost Optimization